Table of Contents
Concrete VS. Cement | Are Concrete and Cement the same?
The direct answer is “NO.” Cement can be introduced as a binder or else as an adhesive material used to bind other constituents of a mixture together. In other words, cement is an ingredient of concrete, the so-called mixture.


Concrete Composition | How concrete is made?
Concrete is a heterogeneous composite mixture used as a main construction material. Concrete is mainly composed of cement, water, and aggregates. A mixture of cement and water alone is called a “mortar.” In addition to the main ingredients, several other materials are added to concrete based on the requirements. They are the mineral admixtures, chemical admixtures, and other materials such as pigments (liquid or dry pigments), fibers (synthetic, steel, glass, or carbon), and fillers (limestone, excess pozzolan). In waterproofing, we add additional chemicals to increase the durability of concrete.
Concrete Grade | What is grade of concrete?
The grade of concrete is defined as the expected minimum compressive strength of concrete at 28 days with adequate quality control. The grade of concrete is selected based on several requirements such as structural needs, service life conditions, aesthetics, construction requirements, availability of materials locally, cost effectiveness, etc. In addition to these main requirements, there are a few other characteristics that affect the technical selection of a concrete grade. They are the setting time, freeze-thaw resistance, shrinkage, permeability, and abrasion resistance. Generally, the following criteria are followed when selecting the grade of a structural member of a high-rise building:
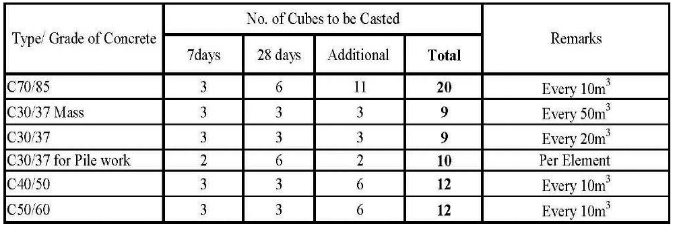
Concrete Grade Requirements
| Grade | Structural Element |
| C30/37 Mass | Foundations, Foundation beams, Pile caps |
| C 30/37 | Beams, Slabs and Stairs |
| C 30/37 (Low slump) | Ramps |
| C40/50 | Cores, Shear walls |
| C50/60 | Columns, Plinth in pile cap |
| C70/85 | Columns (external/ substructure) |
Concrete mix ratio and the required number of cement bags
The concrete mix ratio is the cement: sand: aggregates (usually 19mm metals) ratio used in preparing concrete. Please note that the ratios below are for the cement class of 32.5 MPa.
| Concrete Grade | Mix Ratio | No. of cement bags |
| G15 | 1:3:6 | 4.5 |
| G20 | 1:2:4 | 6.5 |
| G25 | 1:1.5:3 | 8.0 |
| G30 | 1:1:2 | 11.5 |
Concrete Slump | What is the slump of concrete?
The slump test must be conducted as soon as a concrete truck gets on-site to determine the flow, consistency, and workability of fresh concrete. The slump of concrete is simply the ease with which it can be poured and compressed without segregation.
Slump Test | How to test for concrete slump? Testing for fresh concrete should be carried out in accordance with BS EN 12350-2
The nominal slump is measured as (200±25mm) in high-rise building construction while (125±25mm) in road and other construction.
General Procedure of Slump Test
Objective: To check the workability or consistency of fresh concrete.
The apparatus consisted of a mold with a base diameter(200±2mm), top diameter(100±2mm) and height(300±2mm), a base plate of 450mm*450mm and a tamper rod with diameter of 16mm and height of 600mm.

Procedure:
- Initially, the mold, free of any debris, is placed on the base plate and a concrete sample is taken from the ready-mix truck.
- While the operator keeps standing on the 2-foot pieces of the mold, the mold is immediately filled with three separate layers, each layer being approximately 1/3 of the mold height.
- Each layer should be rodded with 25 strokes of the tamping rod.
- After pouring and rodding the top layer, the concrete surface should be struck off using the tamping rod.
- The mold is then immediately raised steadily upward, a distance of 300 mm in 5
2 seconds.
- The slump is measured as the vertical distance between the mold top and the displaced origin of the sample.
- The test should be completed within 2 & 1/2 seconds.
Cube Test | How to test the grade (compressive strength) of concrete
Cube test is used to determine the concrete compressive strength. To begin with, the contractor’s concrete cubes must be made, cured, and then brought to the lab in accordance with BS EN 12390–2. Following that, the required material’s density and compressive strength are determined in accordance with BS EN 12390–7 and BS EN 12390–3 respectively. The testing procedure must comply with the National Structural Concrete Specification (NSCS).
Cube Test | How to test the grade (compressive strength) of concrete
Cube test is used to determine the concrete compressive strength. To begin with, the contractor’s concrete cubes must be made, cured, and then brought to the lab in accordance with BS EN 12390–2. Following that, the required material’s density and compressive strength are determined in accordance with BS EN 12390–7 and BS EN 12390–3 respectively. The testing procedure must comply with the National Structural Concrete Specification (NSCS).
General Procedure of Cube Test
Objective: To check the compressive strength of concrete
The apparatus consisted of a 150mm*150mm*149mm cubical mold, a metal rod, and a compressive strength testing machine.
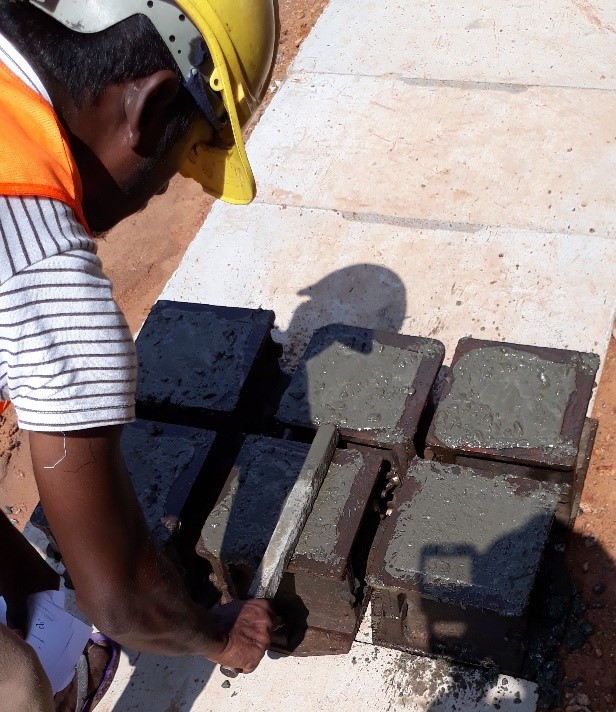


Procedure
- Initially, the mold must be grout sealed with grease and the base plate must be tightened well.
- Then concrete is poured into the mold in 3 layers, where each layer is approximately 1/3 of the mold height.
- Each layer is then rodded with 35 blows using a tamper to prevent air from being trapped inside, which results in voids in the concrete.
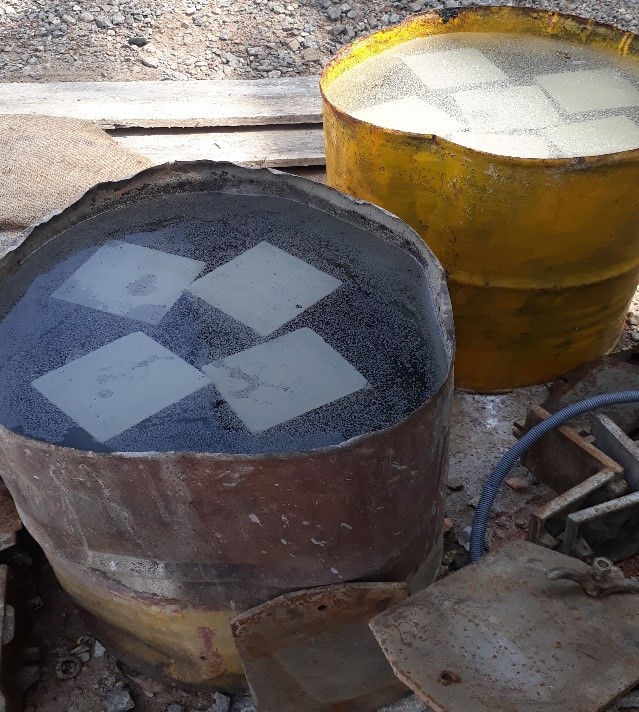
- After 24 hours of casting, the mold is removed, and the test specimens are immersed in a water bath for curing.
- After 7 or 28 days of curing, the specimens will be taken out and tested in a compressive testing machine.
- In a compressive testing machine, a gradual load is applied at a rate of 140kg/cm2 or similar until the specimens fail.
- The load recorded at the failure divided by the area of the specimen is then taken as the compressive strength of concrete.
What are concrete casting equipment?
These are the equipments used for casting of concrete. The casting equipment consists of a CPB (Concrete Pumping Boom), a fixed pump, a casting pipe, and a detachable pump. Additionally, the pump car serves as the driving unit for the concrete, while the concrete truck serves as the transport and temporary storage unit. Porkering will be accomplished with a mechanical vibrator.
General process of concreting
- Wash off the screed surface to remove mud and dirt.
- Apply form oil (diesel+grease) over the form work to easify deshuttering.
- Make the formwork leak-proof by inserting sponge sheets into the gaps.
- If the concreting is carried out against a previously laid slab, first chip the construction joint (CJ) of the existing slab and apply a moisture-preventing boding agent like BARRA EMULSION 57D. That prevents the absorption of moisture into the previously laid concrete and easifies the process of bonding between the old and new concrete.
- Pour concrete using the pump, not exceeding a height of 1.5m to prevent any segregation. If the concrete is directly poured from the ready-mix truck, then a chute and an angled board are required to maintain the concrete’s falling height below 1.5 m.
- Then spread the concrete using a showel.
- Carry out pokering nearly 500 mm apart to achieve the maximum possible concrete density by elliminating air bubbles.
- A compacted layer’s thickness is typically kept under 300 mm.If the concrete has to be laid in two layers, the porker should be inserted only up to 3/4th of the 2nd layer to prevent any disturbance to the first layer, which has already been compacted.
- Then the surface is leveled and cut.
- Finally, curing is carried out by spraying water or any other means.

Curing | What is concrete curing?
Curing is carried out immediately after placing and finishing concrete for a minimum of seven days. It helps to maintain the desired moisture and temperature of the concrete and prevents cracking. The initial curing affects about 65% of the initial strength gain (the 28-day strength).
What are the different methods of curing concrete?
- Immersion
- Ponding
- Covering with sheets (Hessian or plastic sheets, kept damp and 1000-micron polythene)
- Laying water-retaining covers such as wet gunny bags.
- Continuous spraying of water.
- Spraying CHRYSO cure AC which is an acrylic based curing agent with adhesive properties in emulsion.
- A combination of all of these methods.

Concrete Cover | What is concrete cover?
In reinforced concrete, the concrete cover is the minimal distance between the surface of embedded reinforcement and the concrete’s exterior surface. The concrete cover is often retained for the following reasons:
- To add aesthetic value.
- To shield the steel reinforcing bars from the impacts of the environment in order to avoid corrosion.
- To provide thermal insulation for the reinforcing bars, which is necessary to defend them from catching fire, etc.
- To anchor reinforcement bars enough to allow them to be stressed without sliding.
When selecting a concrete cover for a structural element, the following approach has often been followed:
- Earth retaining walls and water tanks: 30 mm
- Inside building cores, shear walls, slabs, and stairs: 30 mm
- External cores, shear walls, slabs, and stairs: 40 mm
- Inside building beams and columns: 35 mm
- External beams and columns: 45 mm
- Foundations and foundation slabs: 45 mm
- Foundation beams and pile caps: 50 mm
- Piles: 85 mm
Clear cover, Nominal cover VS Effective cover of concrete | How to calculate the clear cover, nominal cover, and effective cover
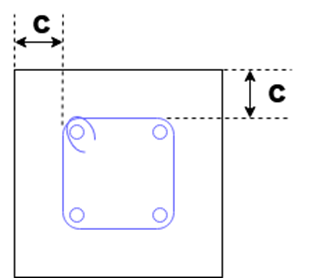
The clear cover is the distance between the outer concrete surface and the outer surface of the adjacent reinforcement bar. If there are links or stirrups in addition to the main bar, then the cover should be maintained not from the main bar but from the respective link or stirrup. Otherwise, no adequate cover will be available for the particular link. Typically, the nominal cover exceeds the diameter of the reinforcement bar. Sometimes, the clear cover is also called the nominal cover.
Let’s consider a typical cross section of a column as shown below. The clear cover of concrete is denoted by “C”.
Effective cover is the distance between the outer concrete surface and the center of the main reinforcement bar. Let’s consider a situation where the diameter of the main bar is ∅D and the diameter of the stirrup is ∅d.
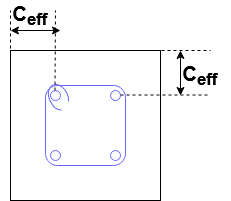
Then the effective cover = clear cover + stirrup diameter+( diameter of the main bar/2).
Ceff = C + ∅d+( ∅D/2)












